0102030405
PTW wall production technology
2024-11-22
Samsung's China semiconductor project features innovative prefabricated structures like the UT and CT buildings, utilizing 1,165 components and PTW technology for efficiency and quality. PTW's factory-based production speeds construction, enhances wall quality, and reduces costs.
1. Project Overview
Project name: Samsung (China) Semiconductor Co., Ltd. 12-inch flash memory chip phase II project, 3 buildings outside the power station; Unit name: UT® (China's first assembled high-tech factory power station), CT building (China's first assembled high-tech factory cooling tower); Structural form: assembled integral reinforced concrete frame structure; Unit number of floors: UT building has one underground floor and two above-ground floors, CT building has one underground floor; Type and quantity of components used: 1,165 prefabricated columns, composite beams, composite slabs and PTW (double skin walls).
2.PTW wall structure system
The Precast Truss Wall (PTW) for factory buildings is a new technology and process introduced and absorbed from abroad. It has been applied in my country's construction market and is being promoted. The structure consists of two parts: "prefabrication" and "cast-in-place". The prefabrication part consists of two prefabricated reinforced concrete slabs (connected by steel trusses). The prefabrication part is installed on the construction site to form a wall with a "cavity". Finally, steel bars are arranged in the "cavity" and concrete is poured to form a complete wall. It is mainly used in sewage treatment plants, underground parking lots, warehouses, rainwater storage tanks and other projects.
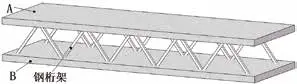
3. Advantages
(1) Most of the wall pouring work of PTW is completed in batches in the factory, which reduces a lot of work on the construction site and greatly shortens the total construction period of the project.
(2) Thick concrete walls are difficult to maintain and prone to cracks. The use of double-skin walls can avoid such problems; the concrete strength and appearance quality of the "prefabricated" part are relatively high, which can greatly improve the final strength and appearance quality of the wall.
(3) The "prefabricated" part can serve as the formwork of the wall during the on-site construction stage, completely avoiding unsafe factors such as mold expansion and mold running.
(4) The "prefabricated" part is mass-produced in the factory, which can minimize the total cost of the wall per unit area.
4.Production process flow
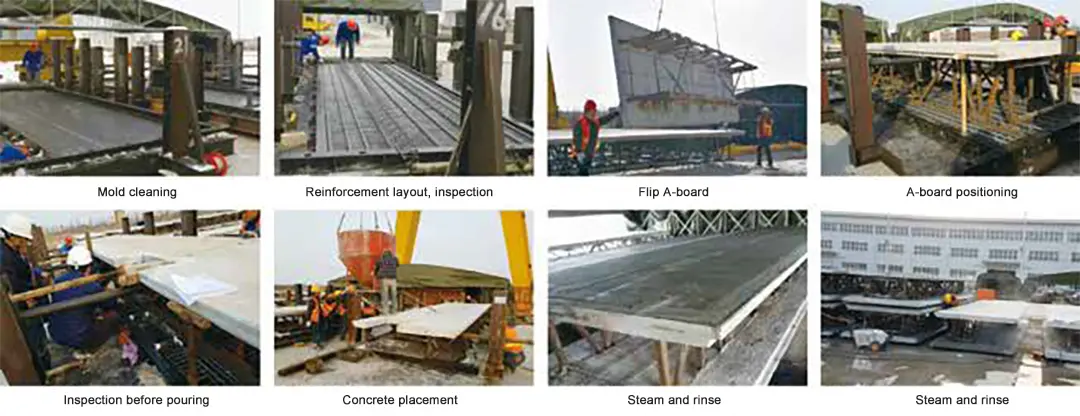
The production of PTW wall is divided into A plate production and B plate production, and its production process is as follows:
A plate production: (1) Cleaning the mold, assembling the mold, and applying the release agent. Before assembling the formwork, it should be cleaned up, especially the mortar and adhesive strips at the joints of the formwork should be cleaned up, and foam plastic strips should be attached to the joints to ensure that there are no gaps and no shrinkage during installation. During the process of assembling the formwork, the side formwork must not be dragged on the bottom formwork, and the bottom formwork or side side must not be hammered with tools.
Select the appropriate release agent according to the technical requirements, stir it evenly before using it, apply it evenly, and do not miss any spots. Protective measures should be taken, and the application of the release agent must not discolor or damage the concrete surface.
(2)Place the steel mesh, embedded parts and steel trusses. The frame should be lowered vertically from the top of the formwork and should not be dragged on the formwork surface. Long frames should have more hanging points to avoid local deformation of the steel bars. Adjust to the appropriate protective layer thickness after entering the mold. Embedded parts should be accurately positioned. The embedded parts on the bottom or casting surface are fixed with magnetic bolts or pressure bars. It is strictly forbidden to walk on the steel bars after they are put into the mold. It is forbidden to reprocess the high-strength steel bars after they are bent.
(3)Concrete pouring. Before pouring concrete, the debris in the mold should be cleaned up. Flat plate components are vibrated and formed by a vibrating table, and high-top components are vibrated and formed by a vibrating rod. The vibrating rod is inserted to cooperate with the vibration. The time of vibration should be controlled. The ribbed flat plate is poured with concrete in two times. The plate surface is poured first, and then the plate rib part is poured after the hanging mold is placed. After pouring and forming, the upper surface should be smoothed.
(4)Curing. The method of static stop for 1h + heating for 2h + constant temperature for 3h + cooling for 2h is adopted, and the maximum temperature is 60℃. During steam curing, the heating rate shall not exceed 20℃/h, the maximum temperature shall not exceed 65℃, and the cooling rate shall not exceed 20℃/h. The curing time is preferably 8 hours, and the specific curing time is determined according to the site environment. After steam curing, the temperature should be lowered to a temperature difference of no more than 25°C between the component surface and the outside. Natural curing should be carried out for 2 to 3 hours before steam curing.
(5)Demolding and flipping. When the strength of the concrete test block cured under the same conditions reaches at least 75% of the design strength, demolding and lifting can be carried out. Before demolding, all temporary fixings for fixing embedded parts, dowel bars and embedded bolts should be removed without omission. The demolding of the component should be vertical and stable, and no bumps should be made to avoid damaging the corners. After the component is demolded, it should be placed on a wooden block wrapped with a foam pad and then flipped. The flipping of the component is carried out with a special flipping machine.

Production of B plate: (1) The steps of cleaning the mold, assembling the mold, applying the mold release agent, placing the steel mesh and embedded parts are the same as those of A plate.
(2)Installation and alignment of A plate. According to the position requirements of the drawing, install the A plate and use the mold fine-tuning nut to adjust the position. During the alignment process, be careful not to knock the corners and finished surfaces of the components to prevent damage to the components. During the alignment process, use a plumb bob to check the relative positions of the A and B plates. If the misalignment exceeds the requirements of the specification, adjust it immediately.
(3)Concrete pouring and curing of B plate are the same as those of A plate.
(4)Renovation and storage. After the components are demolded and turned over, they should be properly trimmed. After trimming, the surface should be smooth, the edges and corners should be neat, and the color should be basically consistent. The stacking site should be flat, solid, and well-drained. The wooden blocks for stacking components should be wrapped with plastic film to prevent the color of the wood from contaminating the board surface after rain.