What to use for concrete shuttering?
The choice of materials for concrete shuttering depends on the type of construction, desired finish, budget, and the project’s requirements. Common materials include:
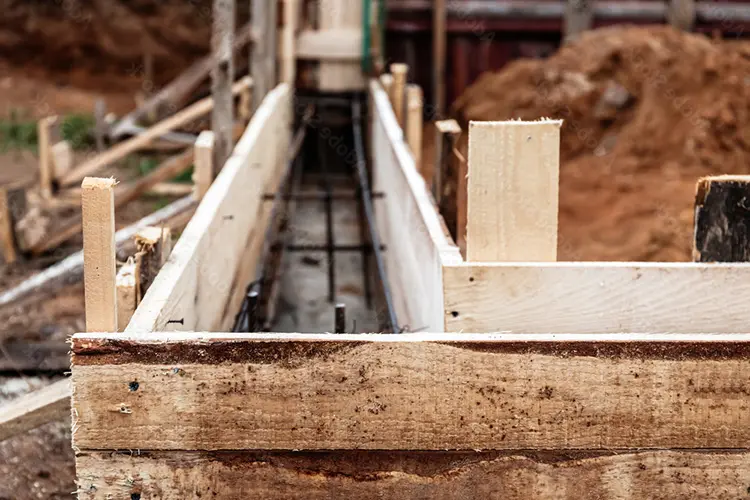
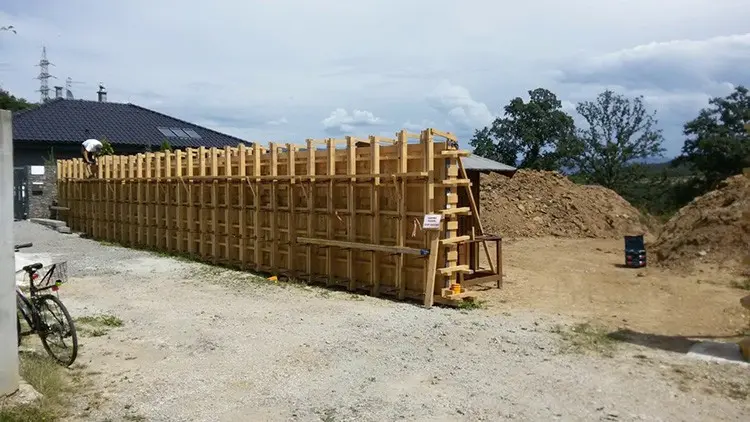
1. Timber (Wood)
●Advantages:
●Lightweight and easy to handle.
●Can be easily cut and shaped for custom designs.
●Readily available and relatively inexpensive for small projects.
●Disadvantages:
●Limited reusability (typically 5-10 uses).
●Can warp or deform when exposed to moisture.
●Requires treatment for durability.
●Best For: Small-scale projects or projects requiring custom shapes.

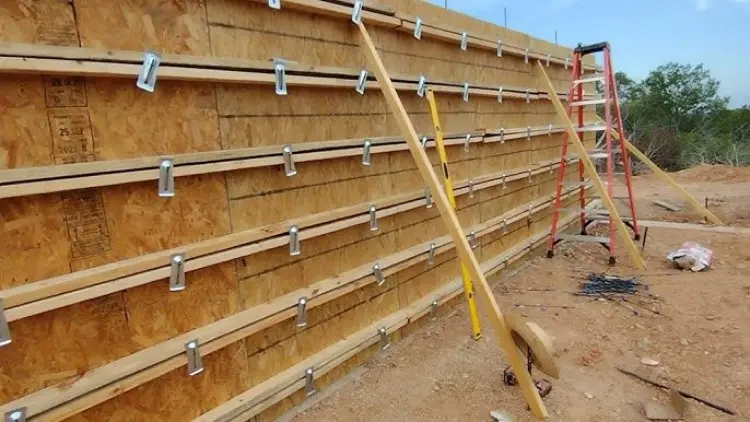
2. Plywood
●Advantages:
●Smooth surface for better concrete finish.
●Moderately reusable (10-15 times).
●Available in various thicknesses.
●Disadvantages:
●Susceptible to water damage unless treated.
●Requires careful handling to avoid splitting.
●Best For: Medium-scale projects and structures with smooth surface requirements.

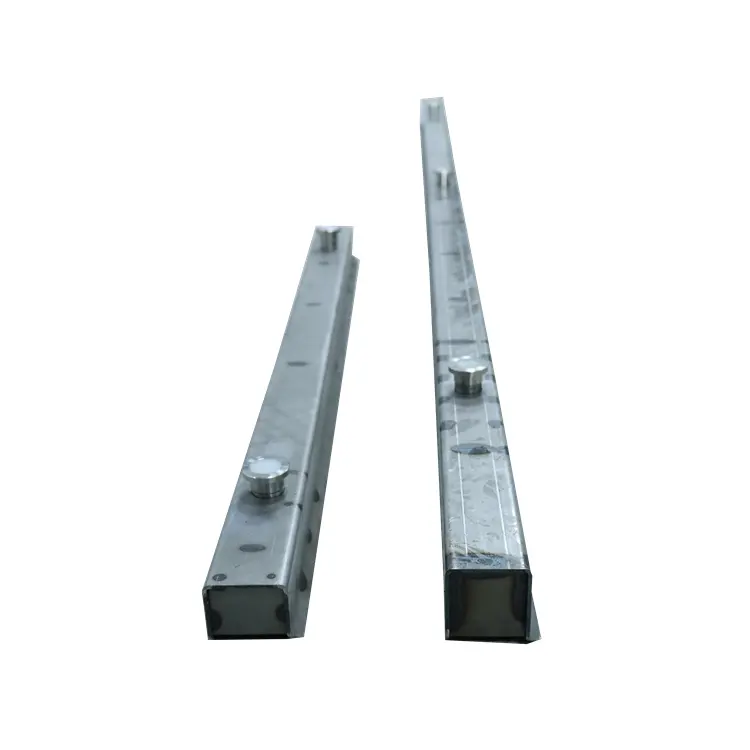
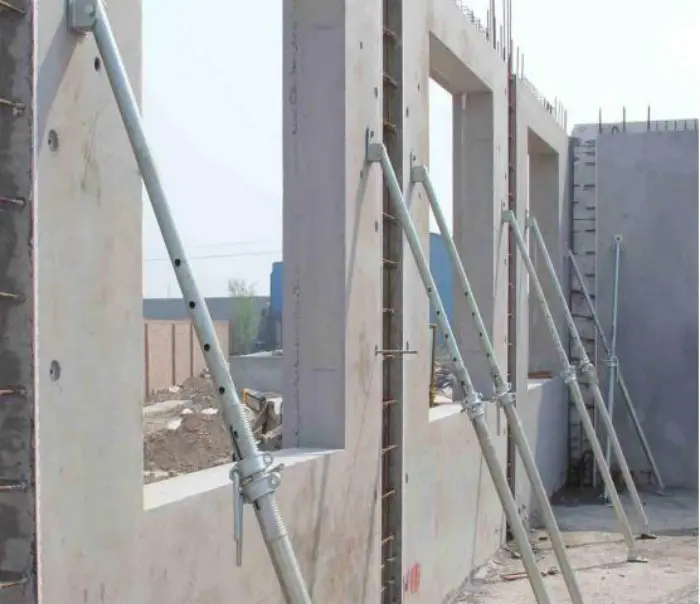
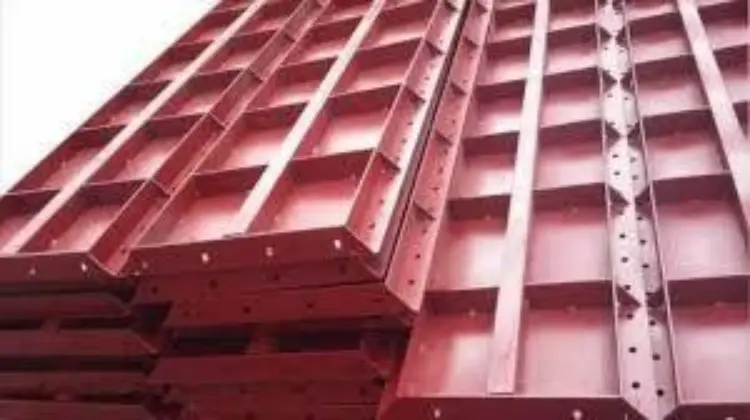
3. Steel
●Advantages:
●Extremely durable and reusable (up to 100 times or more).
●Provides precise shapes and dimensions.
●Resistant to moisture and easy to clean.
●Disadvantages:
●Expensive initial investment.
●Heavy and requires skilled labor for installation.
●Best For: Large-scale projects and repetitive construction.

4. Aluminum
●Advantages:
●Lightweight compared to steel.
●High reusability and corrosion resistance.
●Disadvantages:
●Expensive and less flexible for complex shapes.
●Can react with wet concrete if not properly coated.
●Best For: Medium to large projects with repetitive forms.
5. Plastic or Fiberglass
●Advantages:
●Lightweight and easy to handle.
●Durable and water-resistant.
●Ideal for curved or decorative shapes.
●Disadvantages:
●Higher initial cost.
●Limited availability in some areas.
●Best For: Projects requiring unique shapes or decorative finishes.
6. Fabric Formwork
●Advantages:
●Flexible and adaptable for complex shapes.
●Lightweight and easy to install.
●Disadvantages:
●Single-use in most cases.
●Not suitable for standard forms or heavy-duty projects.
●Best For: Architectural and artistic designs.
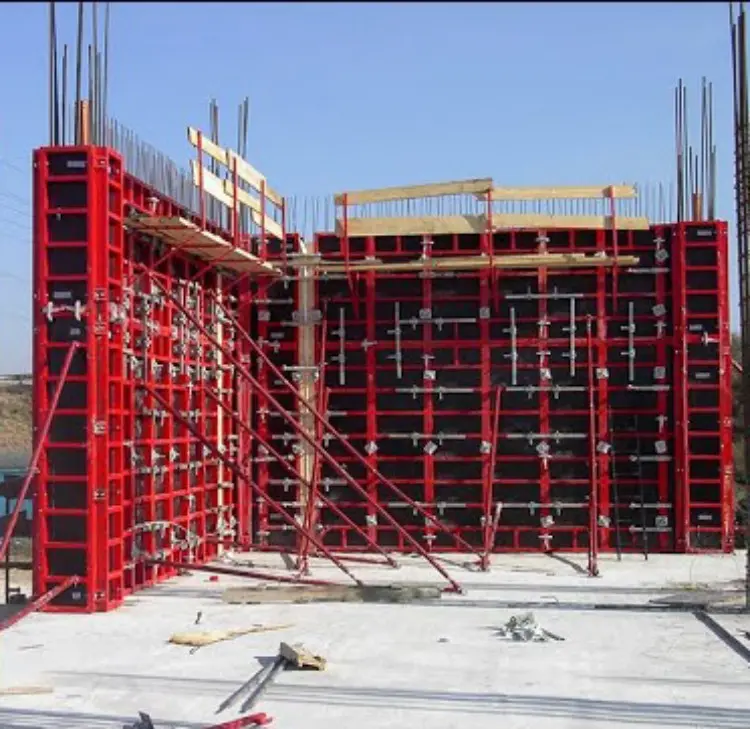
7. Modular Systems
●Description: Prefabricated systems made of steel, aluminum, or plastic.
●Advantages:
●Quick to assemble and disassemble.
●Highly reusable.
●Reduces labor costs.
●Disadvantages:
●High initial cost.
●Limited customization options.
●Best For: Large-scale and repetitive construction projects.
Choosing the Right Material:
●For Small Projects: Timber or plywood is economical and sufficient.
●For Large Projects: Steel or modular systems are more efficient and durable.
●For Special Shapes: Plastic, fiberglass, or fabric formwork offers flexibility.
●Budget Constraints: Plywood is a good compromise between cost and performance.