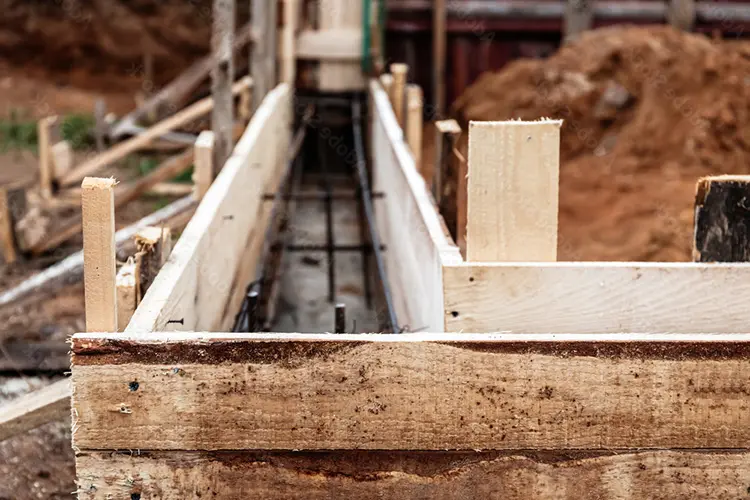

What to Use for Concrete Formwork? Let’s Break It Down Like a Pro
An experienced prefab and formwork expert offers practical advice on formwork choices. Wood is cheap and flexible for small jobs but warps. Steel suits repetitive, high - rise projects with its durability and speed. Aluminum is lightweight, reusable for complex designs, though costly upfront. Match the material to your project type for best results.

What to use for concrete formwork?
A 15 - year concrete pro shares formwork wisdom. Details materials, tools, cost - slashing combos, and mistakes. Highlights prep’s key role, inviting readers to share their formwork tales.

How Long Before Stripping Concrete Forms in Precast Production: A Practical Guide
This practical guide explores optimal stripping times for precast concrete forms (12–24 hours), influenced by mix design, curing methods, and element complexity. Magnetic formwork systems—like shuttering magnets and robotic demolding tools—enable faster cycles (e.g., 14-hour stripping) while enhancing precision and durability. Best practices include maturity testing, temperature management, and case studies showcasing 82% production boosts through magnetic tech adoption.
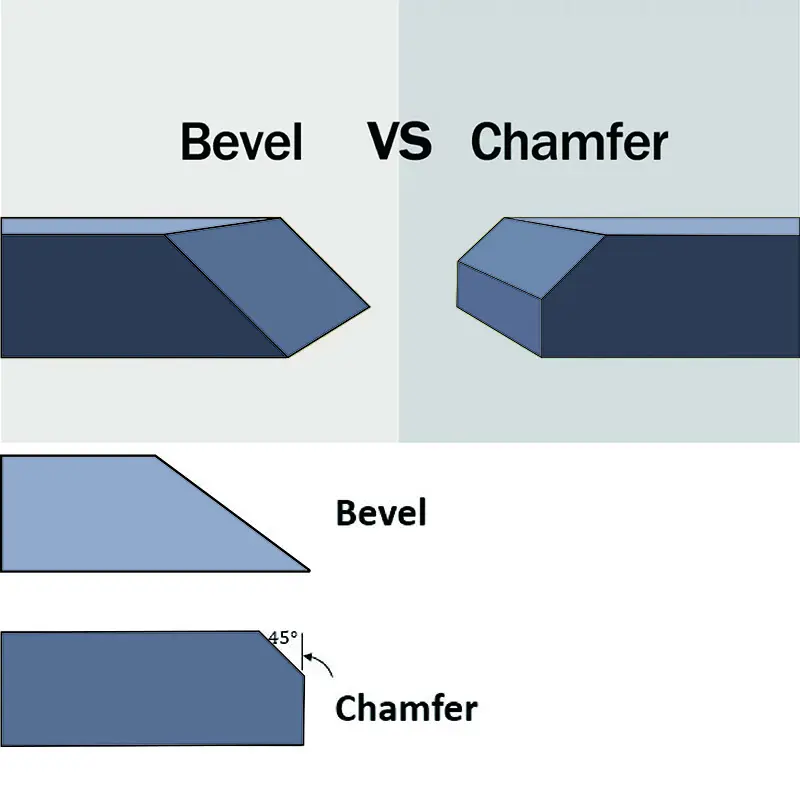
Understanding Bevel vs. Chamfer in Precast Concrete: What Contractors Need to Know
This article explores the critical roles of bevels and chamfers in precast concrete, explaining their distinct functions, angles, and applications. Bevels (angled >45°) enhance durability, aesthetics, and safety, while chamfers (45° flat cuts) improve mold release, alignment, and structural integrity. Innovations like magnetic steel chamfers revolutionize efficiency through reusable, corrosion-resistant solutions that save time and ensure precision. Contractors learn how to choose the right edge treatment based on project needs, balancing aesthetics, safety, and structural performance.

How to Edge Concrete Like a Pro: A Step-by-Step Guide with Magnetic Chamfer Strips
This step-by-step guide explains how to achieve professional concrete edges using magnetic chamfer strips, highlighting their types, benefits, and application process. Chamfering enhances durability, safety, and aesthetics, while magnetic strips—steel, urethane, or PVC—offer precision, reusability, and ease of installation. The guide covers tool selection, preparation, pouring techniques, and maintenance tips, emphasizing their superiority over traditional methods for both DIY and industrial projects.
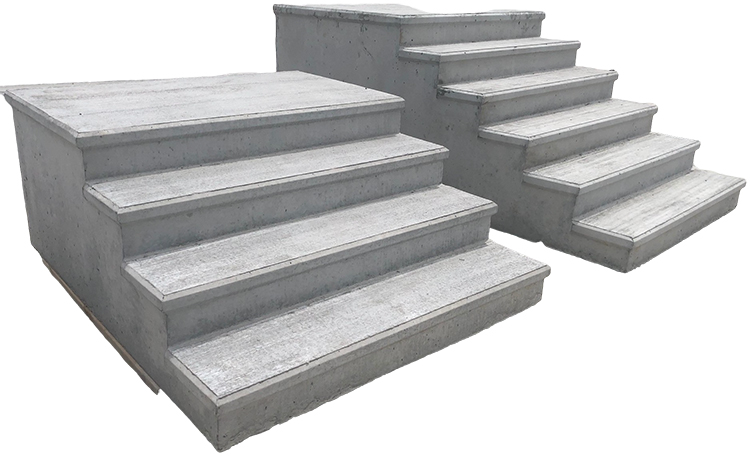

How to Install Precast Concrete Steps: A Step-by-Step Guide for Professionals
Precast concrete steps are durable and cost - effective. This guide details installation steps from pre - installation to post - installation, including site assessment, step positioning, and safety enhancements. QCM's magnetic formwork systems can improve production and address common installation issues.
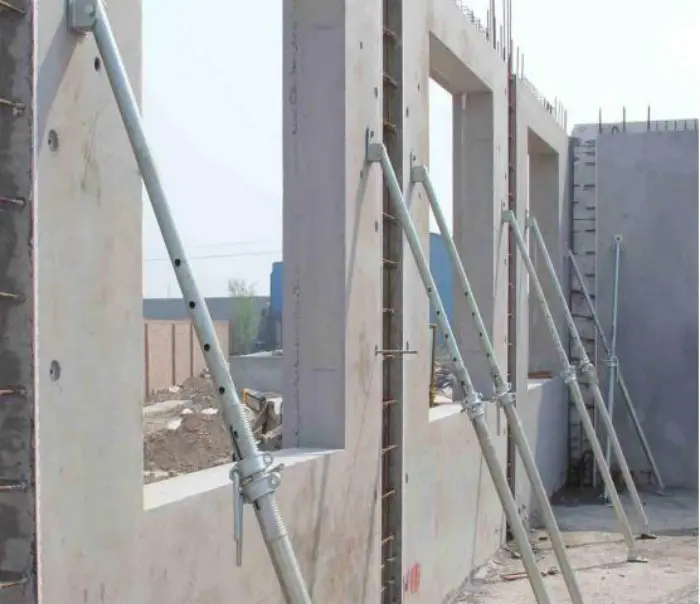

How do you join precast concrete panels?
Precast concrete panels are crucial for large structures. They're made off-site and assembled on-site. Various joining methods exist, like bolted, welded, grouted, dowel, tensioned cables, slide-in, clips, and sealant joints. Each has pros and cons. The choice depends on factors such as load-bearing, seismic and wind load, assembly time, and durability. Proper design and engineering are key for stable and durable structures.
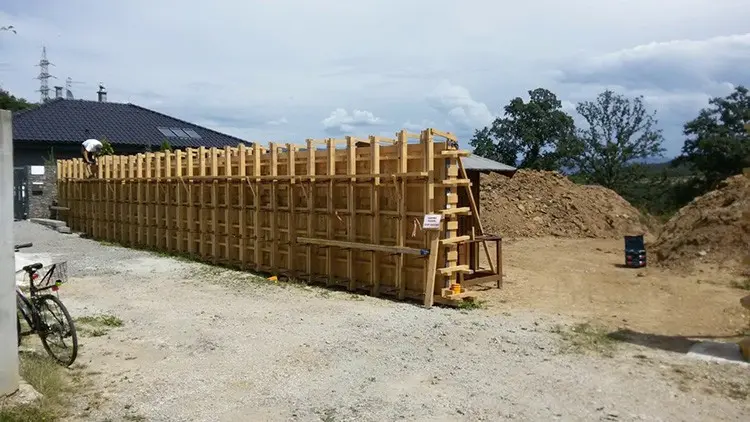

What to use for concrete shuttering?
Concrete shuttering material selection depends on the project type, finish, budget, and requirements. Common options include timber, plywood, steel, aluminum, plastic, fiberglass, fabric, and modular systems. Timber is economical for small projects, while steel and modular systems excel in large-scale construction. Plywood offers a balance of cost and performance. For special shapes, plastic, fiberglass, or fabric formwork provide flexibility.
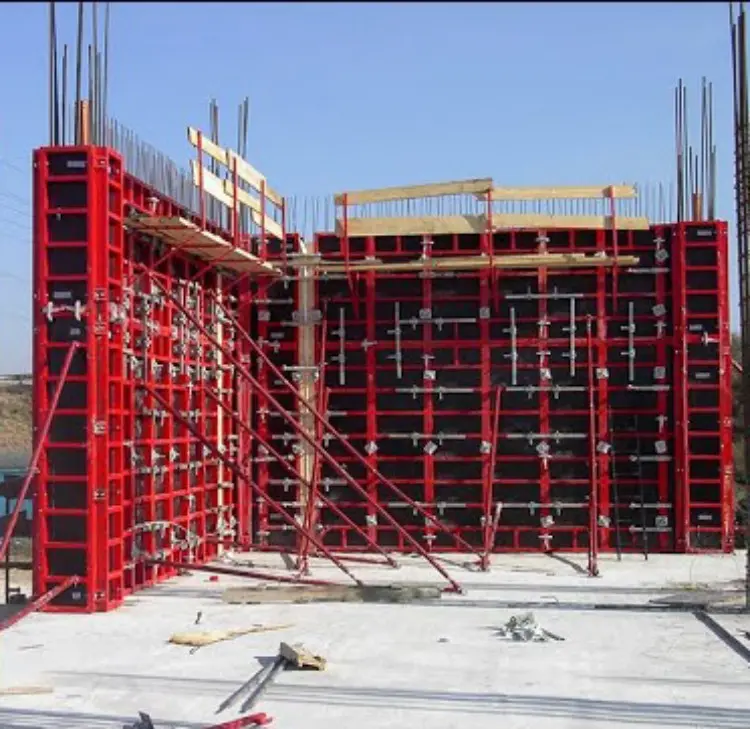

What is the purpose of shuttering?
Shuttering, or formwork, is a temporary structure used in construction to shape and support poured concrete or other materials as they harden. It acts as a mold for concrete, providing support, ensuring a smooth surface finish, and maintaining structural integrity. Common materials include timber, plywood, steel, and plastic or fiberglass. Once concrete gains strength, shuttering is removed in a process called stripping.
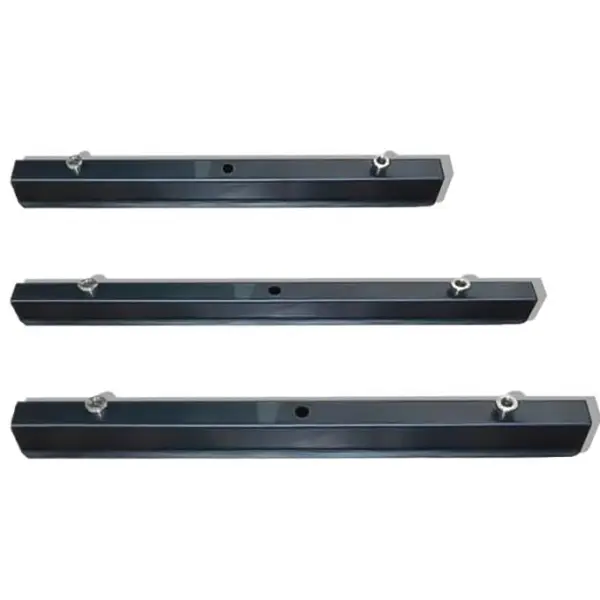

What is Magnetic Shuttering System ?
This article introduces a magnetic shuttering system for precast concrete. It details its technical aspects like sizes and materials, operation principle via magnetic suction cups. It also highlights advantages such as easy installation, precise positioning, reusability, and strong environmental adaptability.
